Product Rule Concepts
Concepts
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Product Option | It is the list of possible values for a parameter (dimensions, products, etc.). For example, the "handle" option of a product will define the list of possible handle product references that could be used for a cabinet. |
| Product Rule | It gives the opportunity to create dependencies between two or more options of the same product. |
Product Rule Definition
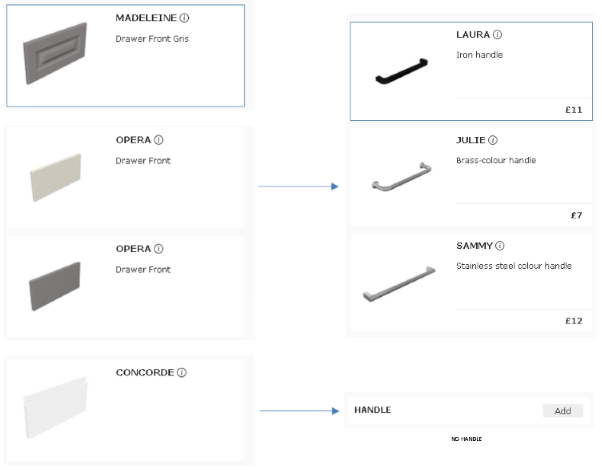
On business definition, on the same cabinet there is a dependency between front and handle products: some fronts have a "handle" already integrated in the front geometry. Consequently, the handle component needs to be removed when those fronts are chosen on a cabinet. To manage this dependency, the ByMe platform data model allows creating a compatibility table between two or more options of the same cabinet. Once done, each time the cabinet will be updated in the planner by the customer, the rules will be applied to set up only compatibles values. To come back to the front / handle relation, each time the customer will change the front in a cabinet, then the handles will be updated with only compatible values defined by a product rule.
❗️ Please note that a product rule allows to set up relation between options of the same cabinet. If the link is about two cabinets or a cabinet and its environment, then we will use an applicative rule 🔗.
To be valid in the ByMe platform, a product rule needs to be defined by:
- An ID : defined by the range manager, this database identifier is unique.
- A name : defined by the range manager.
- A typeId : "compatible", "chained" or "unconstrained chained", the type defines the rule behavior.
- A list of products : the list of products for which the rule needs to be applied. To be left empty if using the below list of application distributions.
- A list of application distributions : the list of application distributions (so planner) for which the rule needs to be available. To be left empty if using the above list of products.
- A list of product options : which define the parameters managed by the rule.
- A list of values : the compatibility table which define possible values for each parameters in each cases.
Rule Types
Depending on the typeId of the rule, the result in the planner can be highly different even for the same rule.
typeId 1 - Compatibility
The rule defines a strictly compatible behavior between options of the rule.
This means that each time one of the listed parameters are changed then all the others are updated on the same time to set a compatible configuration to the cabinet.
If used, default values of a cabinet need to be valid with the rule definition, if not an error message pop in the planner console.
For example, wall panels rail is available only in defined dimensions and we need on the same time to be able to change dimension or activate / deactivate the rail.
typeId 2 - Chain
The rule defines a priority behavior between options of the rule.
This means that the first option of the rule is driving the values of the others.
If used, all the values of the first options are always available and the others are updated at each update even if it means some values are hidden.
For example, if an integrated handle front is chosen by the customer then all possible values for handles are hidden because not compatible with the current front.
typeId 3 - Unconstrained Chain
The rule defines the same priority behavior between options of a chain rule but by keeping visible the others possible values.
This means that the first option of the rule is driving the values of the others but all other possible values can still be set.
If used, all the values of the first options are always available and the others are updated at each update and other options are set up with a compatible value, then done it still possible to choose another value on the second option.
For example, each time the customer choose a color for the frame (black for example) the corresponding shelf is activated (also black) but it is still possible to force the white shelf instead of the default compatible one. In this case, please note that the frame color is not changed back because the rule still considers the priority order. |
In 3DCloud you can choose between the two first type in a drop-down list.

List of Products
It is possible to define a product rule on a dedicated cabinet or list of cabinets. For example, if the range manager needs to define a rule between the width and depth parameters and does not want this rule to be applied on each cabinet then they can define the list of cabinets where the rule is valid. The expected value here is the ID of the product.
In usual case, product rules are valid for all cabinets of the catalog. In this case, this product list has to be empty, and the list of application distribution must be used instead.

List of Application Distributions
Unlike products, product rules do not need to be set up in a catalog. For a product rule to be deployed into a planner, it can be applied on one or more application distributions directly. The expected value here is the ID of the application distribution. This list and the previous specific product list must be mutually exclusive. If a product rule has to be available for an entire application distribution, the product list must be empty, and vice versa.
Options
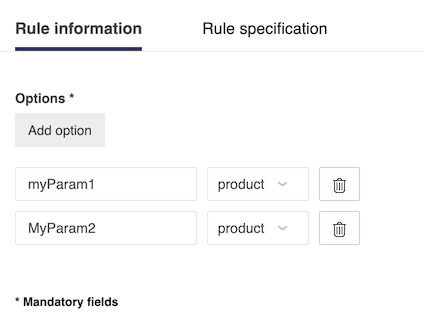
The first step to define a product rule is to list the options managed by this rule. A rule needs at least two options and has no maximum number of options. However, after five options it becomes very complicated to manage all the compatibilities between options. Then it is strongly recommended to split the rule into different rules.
Best Practice
It is better on a range management perspective to have two separate rules to manage front > handle and drawer > handle instead of having only one to manage front > drawer > handle.
❗ To be usable, product options should match already defined parameters on one or more products exactly by its name and type.
Recommendations
To be applied on a product, all the parameters of a rule should be defined on the corresponding product.
For example, a rule between front > leg is not apply on a wall cabinet because there is no leg parameter.
Conversely, if a product parameter values is updated by adding a new front for example, product rules based on front options need to be updated as well.
In a chain rule (typeRule = 2) or unconstrained chain rule (typeRule = 3) context, the order of the options defines the priorities between options.
If the range manager chooses front > handle in this section then the result will be different compared to handle > front in chain context.
Available Options Type
It is possible to use each available type of parameter of the data model (see in the API documentation the section on product rule for more details about expected format):
| Value (integer) | Type |
|---|---|
| 1 | real |
| 2 | integer |
| 3 | boolean |
| 4 | string |
| 5 | color (not used) |
| 6 | material |
| 7 | product |
Values
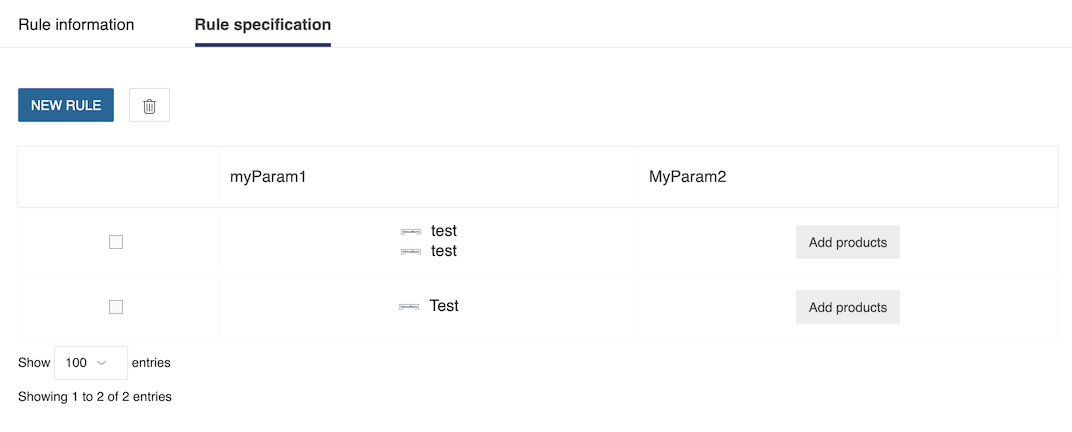
Then, the range manager can define rules values by listing for each options the compatible values. This part has to be considered as a compatibility table where the range manager can add as many row as needed to define all the use cases.
Product Rules in the Planner
When done, product rule is valid and deployed in the planner. Because product rules are applied in the background and always valid, in case of not expected behavior, it is possible to see different messages in the console about applied configuration.
➡️️ Please refer to troubleshooting 🔗 section for more details.
Product Rule Definition via APIs
If the range is managed by APIs, please find hereinafter all the samples needed to provide JSON product rule.
Product Rule Types
{
"ruleTypeID": 2, // Possible values are 1, 2 or 3
}
Product Rule Options and Values
For dimensions (real or integer) in discrete variation.
{
"parameters": [
{
"paramID": "myParamName",
"paramType": 1 // or 2 if the value is an integer
}
],
"compatibilities": [
[
{
"values": [
100,
200,
1000
]
}
]
]
}
For dimensions (real) in continuous variation.
{
"parameters": [
{
"paramID": "myParamName",
"paramType": 1
}
],
"compatibilities": [
[
{
"ranges": [
{
"step": 1, // For real ranges, step is always 1
"maxEx": 100, // Or "max" to include value
"minEx": 10 // Or "min" to include value
}
]
}
]
]
}
❗ Even if max value or min value is not mandatory individually, at least one of them is mandatory.
For dimensions (integer) in continuous variation.
{
"parameters": [
{
"paramID": "myParamName",
"paramType": 1
}
],
"compatibilities": [
[
{
"ranges": [
{
"step": 1,
"maxEx": 100, // Or "max" to include value
"minEx": 10 // Or "min" to include value
}
]
}
]
]
}
❗ Even if max value or min value is not mandatory individually, at least one of them is mandatory.
For booleans
{
"parameters": [
{
"paramID": "myBooleanParamName",
"paramType": 3
}
],
"compatibilities": [
[
{
"values": [
0,
1
]
}
]
]
}
For IDs (products or materials).
{
"parameters": [
{
"paramID": "myIdsParamName",
"paramType": 7 // Or 6 in the case of materials
}
],
"compatibilities": [
[
{
"ids": [
"myID1",
"myID2"
]
}
]
]
}
