Authentication Mechanism
➡️ See POST tokens/ in the API documentation 🔗.
➡️ See also Authenticate your Web Services Request 🔗.
Every call to ByMe API web services needs to be authenticated. There are three ways of being authenticated:
With an API Key / Secret Key. API Keys should only be used in backend system, otherwise the keys would be exposed to the end-user.
With a Legal entity token. The web service caller is identified as a specific Legal Entity. By default, access rights are very restricted (GET methods). This authentication method should be used when no user is logged in.
With a User token. A web service caller is identified as a specific user, associated to a Legal Entity. Access rights are restricted to GET methods and modifications of current user assets.
Note: By default, tokens are generated with read access rights only but you can change this in the web service parameters.
Legal entity and User tokens are JSON web tokens (or JWT) 🔗. JWT do not need to be stored in database, their strings contain everything needed, which reduce the access to the database and the space use.
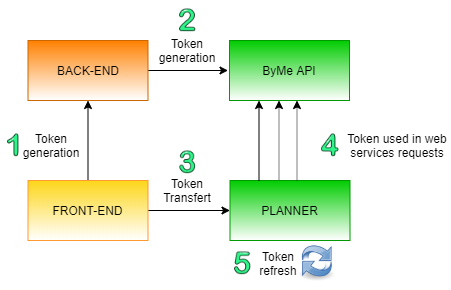
Figure 1 – Token Authentication process
Legal Entity Workflow
No user is logged in.
Front-end asks to its back-end for a Legal Entity token.
The API Key and Secret Key that are associated to the Legal Entity are stored in back-end system to sign the request asking for the generation of a Legal Entity token. To do so, you can see API documentation POST tokens/ 🔗.
Front-end sends the Legal Entity token to the planner via the "Authentication" iFrame message.
The planner uses this token to sign web services request as long as the token is valid.
As soon as the token expiration date is reached, the planner asks for token refresh on the next web service call via a "TokenExpired" iFrame message. Call to Web services will be on hold until it gets back a new token.
➡️ For default timeout period, see POST tokens/ in the API documentation 🔗).
User Token Workflow
The user is logged in.
Front-end tasks to its back-end for a user token.
The API Key and Secret Key associated to the Legal Entity are stored in the back-end system to sign the request asking for the generation of a user token.
Front-end sends the user token to the planner via the "Login" iFrame message.
The planner uses this token to sign web services request as long as the token is valid.
As soon as the token expiration date is reached, the planner asks for a token refresh on the next web service call via "TokenExpired" iFrame message. Call to Web services will be on hold until it gets back a new token.
➡️ For default timeout period, see POST tokens/ in the API documentation 🔗).
