Generic Products
Overview
The concept of Generic Product is the abstract grouping of several products having the same general shape, but different dimensions, colors, descriptions, prices, etc.
An archetypal use-case is to represent a family of kitchen fronts existing in different widths and heights. It is obviously possible to create all family members as distinct ByMe Products, but the Generic Product provides the following benefits:
- Use of a (scalable) 3D resource shared between all the members of the family, which can result in some cases in better performance and easier Range Management
- Ability to reference the family rather than the members, which can create lean user experiences, such as better grouping of items in lists
Defining Generic and Mapped Products
To create such a family in the ByMe platform, the process is:
- Create one ByMe Product carrying the 3D representation - a parametric BMA or scalable BM3 - and all common attributes. It is called the Generic Product.
- Create several "Mapped Products" carrying the specific information of each variation of the Generic Product:
- description, reference, prices, thumbnail.
- Create the mapping relationships between the Generic Product and the Mapped Products, often referred to as "the Mappings" - this is done on the Generic Product.
This can be achieved either using the ByMe API or by using 3DCloud.
Mapping Relationships
The Mapping relationship is defined by:
- The list of parameters used in the relationship. These are the parameters whose values differentiate between the various mapped products.
- The mapping table; each row is a mapping, constituted of:
- a combination of values for each parameters (mandatory)
- a reference to the mapped product (mandatory)
- a priority (optional)
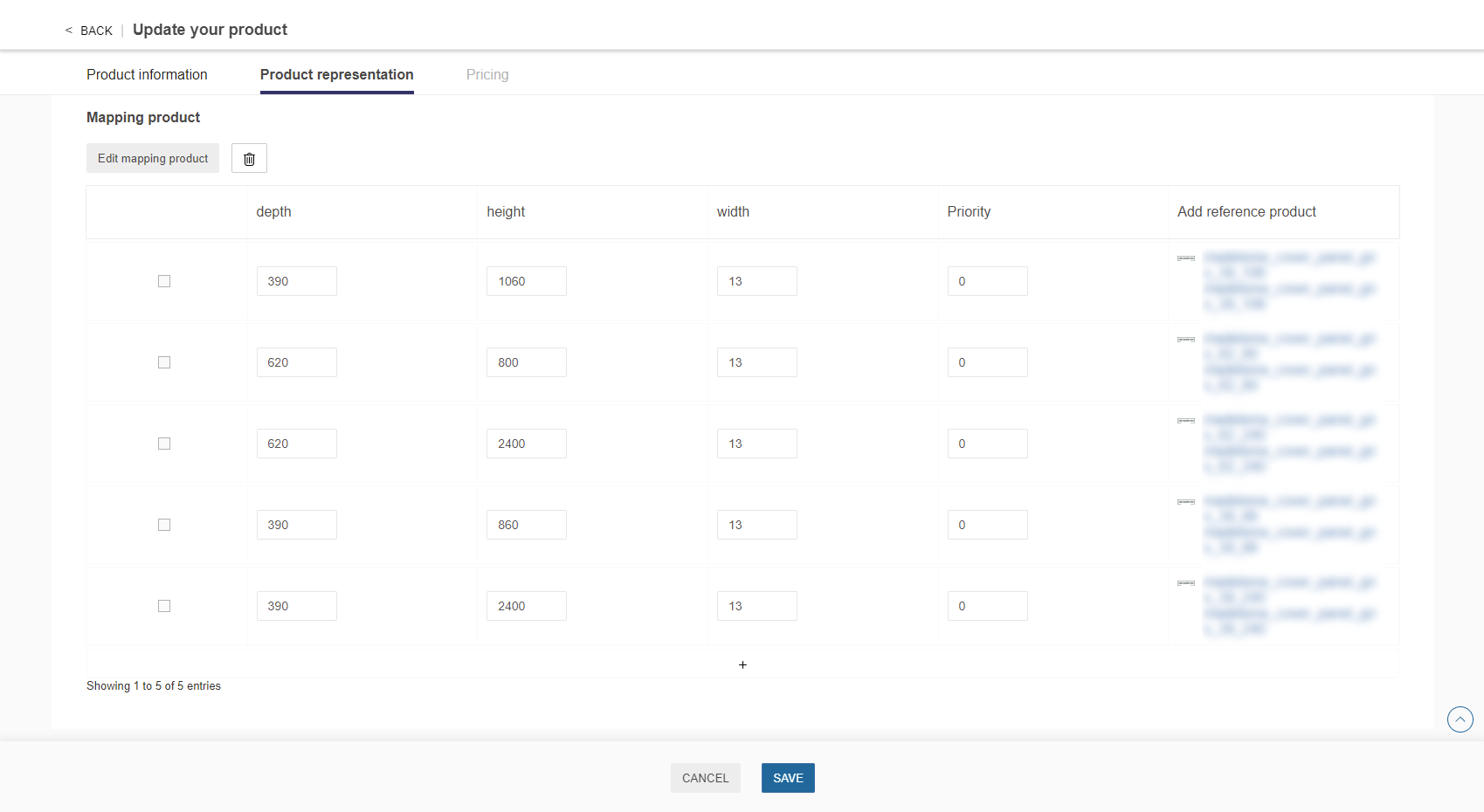
Figure - Mapping example as shown in 3DCloudByMe (The priority attribute is not yet available on this capture)
Note:
- The parameters used in the mapping table must be parameters declared on the Generic Product.
- It is possible to define the same parameter combination in different mappings.
The one with the highest priority will be selected when it comes to solving the mapping.- Contrary, it is not possible to use the same Mapped Product on several parameter combinations.
- We recommend not to declare a parameter whose value is identical on all lines of the mapping table. It will not affect the result and might slow the solving algorithm.
Mapping JSON Object in Detail
Below is detailed the structure of the mappings object to provide when creating mappings through the API.
[
{
"conditions": {
"conditions": [
{
"param": "width",
"value": 400,
"comparison": "EQUAL"
},
{
"operator": "&&"
},
{
"param": "height",
"value": 400,
"comparison": "EQUAL"
}
]
},
"referenceProduct": "2026"
},
{
"conditions": {
"conditions": [
{
"param": "width",
"value": 800,
"comparison": "EQUAL"
},
{
"operator": "&&"
},
{
"param": "height",
"value": 800,
"comparison": "EQUAL"
}
]
},
"priority": 10,
"referenceProduct": "2028"
}
]
Note:
- The only supported operator is "&&" and it means "and". The operator object must be included between each parameter in the conditions array.
- For each parameter object in the conditions array, the keys are:
param: name of the parameter
value: value for the condition
comparison: the only supported value is "EQUAL"- The priority attribute is optional and is used to discriminate the different mapped products that have the same condition values for every parameter. Default value if not given is 0. When solving the mapping, if several mapped products match the input condition, the one with the highest priority will be used.
Runtime Behavior of the Generic Product
Generic Product as a Reference
When the Generic Product is used as a parameter value, it behaves as a reference to the Generic Product, not to any of its mapped products.
If the Generic Product is displayed - for example as a possible choice, in the edit panel of an enclosing product - only the information of the Generic Product is displayed, including the description, which should not carry any variant-specific mention (no dimension, etc.).
Generic Product as an Instance
When the planner needs to create a piece of furniture and all its components, the products are instantiated, and in this context, the ByMe platform attempts to resolve the mapping declared in the Generic Product.
As for all parametric products in the ByMe Platform, the execution context provides values for each of the Product’s parameters - either the default values, or those set by the enclosing assembly, or set by the user in an Edit panel of the application.
When a Generic Product is instantiated in the ByMe platform,
- The values of the parameters required in the mapping table are obtained from the runtime context; if the required parameters are not defined, the mapping is unresolved (see below).
- The ByMe platform performs a lookup of the mapping parameter values in the mapping table of the Generic Product, which designates a particular Mapping Product. It fails if the parameter value combination is not in the mapping table, in this case the mapping is unresolved (see below).
- If the mapping is resolved, the ByMe Platform makes both the Mapped and the Generic Products available to the Application. The general rules are:
- The scene in the 3D planning application mostly uses the Generic Product, its 3D representation, description, thumbnail, etc.
- In this context, the only attribute used in the Mapped Product is the price, in order to calculate the total price of the project; all other attributes of the Mapped Product are ignored, including the 3D representation if any.
- Some behaviors exist outside of the 3D scene, such as the BOM generation, and make extensive use of both the Mapped and the Generic product. These are application-specific, meaning they can be different for Kitchen or Home.
- As an example, the BOM generation would probably use the variant-specific reference, description and prices information, and not this of the Generic Product.
- The scene in the 3D planning application mostly uses the Generic Product, its 3D representation, description, thumbnail, etc.
- If the mapping is unresolved, the 3D scene works well, but the price calculation as well as the BOM are affected. Unresolved mappings should be avoided.
Exposure of the Parameters of a Mapped Product
Parameters of a mapped product are not exposed to a containing entity.
For example, let Front be a Generic Product. In a containing assembly, the expression Front.type is evaluated with Front being the Generic Product, and not the Mapped Product.
This need would arise from situations beyond the design intent of Generic Products - Mapped Products should be limited to: Commercial Information (name, reference, description...), prices, thumbnail, but not parameters not 3D Representation.
Generic Products and Relations
In assembly relations, an expression can contain a term such as Front.width.
This term refers to the "width" attribute of the Product referenced as the "Front" component.
If this product is a Generic Product, the mapping is resolved at runtime and so is the expression. The expression is then evaluated for the value of width on the mapped product.
One important notion to enforce is thus that all mapped products should declare this parameter, or the planner would break.
